NMN: What is it and how does it work?

NMN is everywhere right now. It’s talked about as an “anti-ageing” supplement, an energy enhancer, and even a longevity shortcut. But what actually is NMN, who might it be useful for, and what does human research really show?
Let’s step away from the hype and walk through the facts.
What Is NMN?
NMN (short for nicotinamide mononucleotide) is a compound your body already makes in small amounts. You also get tiny amounts from foods like green beans, broccoli, beetroot, and carrots.
Its main job in the body is helping make something called NAD⁺ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide).
NAD⁺ is essential for:
- Turning food into energy
- Helping cells repair damage
- Supporting normal metabolism and cell function
As we age, NAD⁺ levels naturally decline. That’s what sparked interest in NMN, the idea being that if you provide the body with more NMN, it may be able to make more NAD⁺ again.
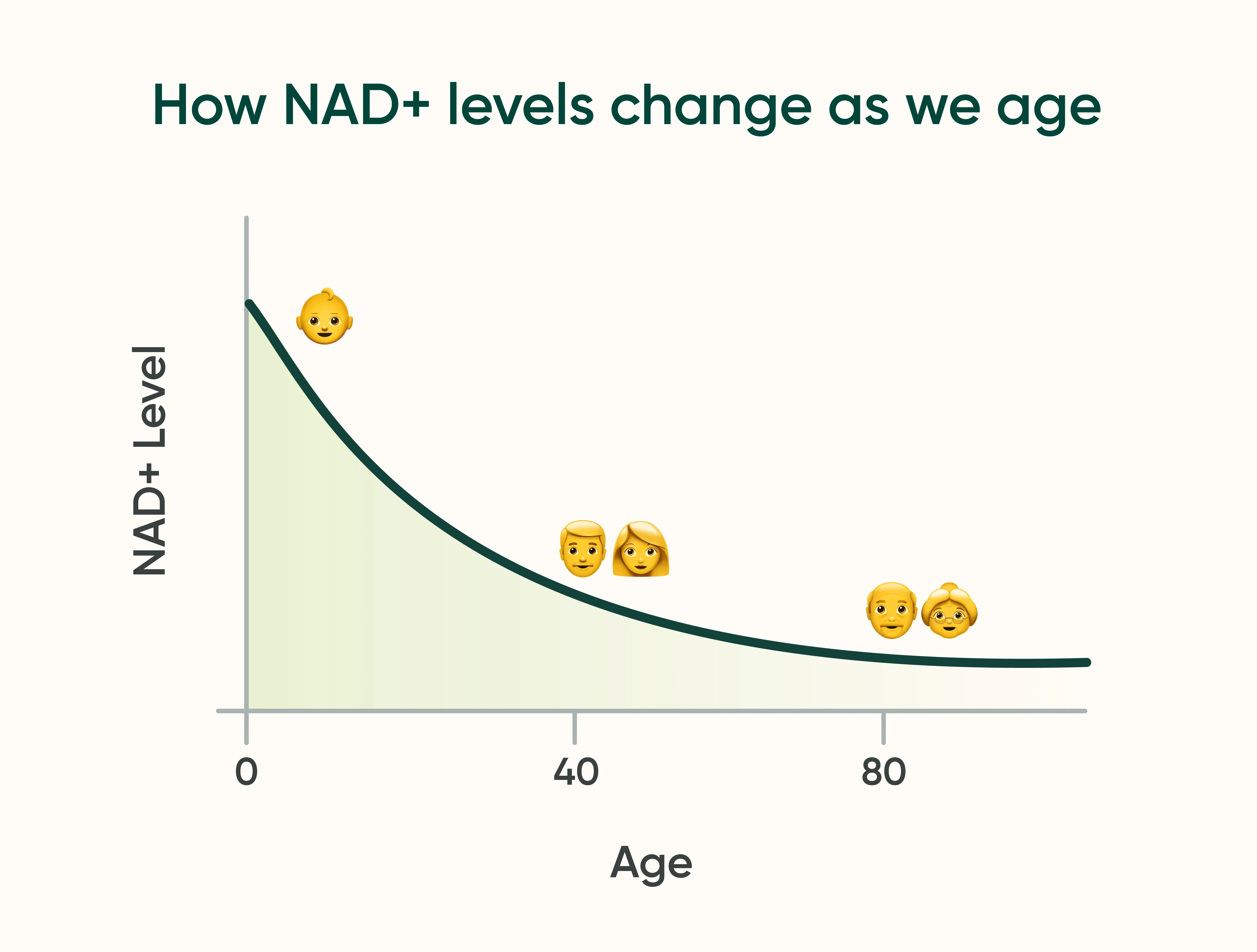
How Does NMN Work?
Think of NMN as a building block.
When you take NMN, your body can convert it into NAD⁺. NAD⁺ is then used inside cells to help them function properly, especially in processes related to energy production and maintenance. So if the goal is more NAD⁺, why not just supplement with NAD⁺?
NAD⁺ isn’t absorbed very well and is usually broken down before entering cells, which is why researchers have focused on precursors like NMN instead.
Human clinical studies have shown that oral NMN supplements do increase NAD⁺ levels in the blood. That part is well supported.
What’s still being studied is what that increase means for long-term health.
Potential benefits of NMN
It’s important to say this upfront: NMN research in humans is still emerging. Most studies are short-term and involve small to moderate numbers of participants, so while early findings are interesting, they’re not enough to draw firm conclusions about long-term benefits or risks. That said, a few consistent themes are appearing.
1. Increases NAD⁺ Levels
This is the strongest and most consistent finding.
Multiple human trials show that NMN supplementation raises NAD⁺ levels safely over several weeks. This confirms that NMN does what it’s meant to do: support production of NAD+ in the body.
What it doesn’t guarantee is dramatic or immediate health changes. Raising NAD⁺ works more quietly in the background, helping support normal cell function over time rather than creating an immediate, noticeable effect.
2. May support physical function as we age
Some studies in middle-aged and older adults have found improvements in measures like:
- Walking speed
- Muscle strength
- General physical capacity
- Enhanced aerobic capacity when combined with intensive endurance training for 6 weeks
These effects tend to be modest and are more noticeable in people who are already experiencing age-related decline, rather than younger, very healthy individuals.
3. Possible metabolic support
There is some early evidence that NMN may help with insulin sensitivity and aspects of metabolic health, particularly in people at metabolic risk. Metabolic risk describes a collection of factors, like excess belly fat and high blood pressure, that can increase risk of stroke, diabetes and heart disease.
However, results are mixed and the human studies are small. Not all studies show improvements in blood sugar, cholesterol, or weight, and NMN should not be viewed as a treatment for metabolic conditions.
4. Longevity and ageing
Much of the interest in NMN and longevity comes from studies in mice. In these studies, NMN has been linked to longer lifespan and improvements in “healthspan,” such as better energy metabolism, physical performance, insulin sensitivity, and slower age-related decline in muscles, cells and blood vessels.
These results have not yet been shown in humans, and that distinction matters.
Mice age much faster than people, and the doses used in animal studies don’t translate directly to human supplements. That said, mouse studies still matter because they help scientists understand how NMN works in the body and guide which benefits are worth testing in human trials. For now, claims around NMN extending human lifespan remain theoretical rather than proven.
Side effects and safety
So far, NMN appears to be well tolerated in short-term human studies.
Reported side effects have been mild and uncommon, including:
- Mild digestive upset
- Headache
No serious safety issues have been reported at commonly studied doses. That said, most studies only run for weeks to a few months. We don’t yet have strong data on long-term use over years.
This is an important gap in the research.
Should you take an NMN supplement?
From an evidence-based perspective:
- NMN does raise NAD⁺ levels in humans
- Some people, particularly middle-aged and older adults, may notice small improvements in physical function
- There is no strong human evidence that NMN prevents disease, slows ageing dramatically, or replaces lifestyle factors
NMN is best viewed as a supportive supplement, not a miracle solution.
People who may be more likely to benefit (based on current research):
- Middle-aged or older adults
- People noticing age-related changes in energy or physical performance
People who should be cautious:
- Those who are pregnant or breastfeeding
- People with chronic medical conditions without practitioner guidance
- Anyone expecting dramatic, rapid results
Australia has taken a positive step by making NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide) available as a legal over-the-counter supplement in listed therapeutic goods. Because of this, NMN products bought outside Australia may not be genuine, high-quality products.
How would you know if it’s helping?
There’s currently no simple test that can show whether NMN is “working.”
Most benefits, if they occur, are subtle and gradual. They’re more likely to show up as:
- Slight improvements in physical capacity
- Feeling a bit more resilient or energetic over time
If someone chooses to supplement, it’s important to assess benefits realistically and avoid stacking multiple “longevity” supplements without professional guidance.
The bottom line
Supplementing NMN has growing human research behind it. The strongest evidence shows that it increases NAD⁺ levels safely in the short term, with some potential benefits for physical function and metabolic health in certain populations.
However:
- Human studies are still limited
- Long-term safety and outcomes are not fully understood
- NMN is not a shortcut to healthy ageing
For most people, NMN sits in the category of “interesting and potentially supportive” rather than essential. Foundational habits like nutrition, movement, sleep and stress management still do the heavy lifting when it comes to long-term health and ageing well.
Reviewed by the Healthylife health experts December 2025.
This article is for informational purposes only and does not provide medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Any information published on this website or by this brand is not intended as a substitute for medical advice. If you have any concerns or questions about your health you should consult with a health professional.
